What Are the Different Methods of Cross Pollination Explain
The two plants genetic material combines and the resulting seeds from that pollination will have characteristics of both varieties and is a new variety. Production of Top-Cross Seed 4.

Pollination Its Types And Comparisons Between Self And Cross Pollination
Cross pollination is a natural method in which transfer of pollen takes place from an anther of a flower of one plant to a stigma of a flower of another plant of the same species.

. Flowering plants need to get pollen from one flower to another either within a plant for self-pollination or between plants of the same species for cross-pollination to occur. Cross pollination and somatic cell hybridisation. Insects cross-pollinate many fruit-bearing plants like apples strawberries raspberries grapes plums and flowers like tulips and daffodils.
The following points highlight the top four methods used in cross-pollinated crops. Those that are pollinated by the wind have long stamens and pistils with small or no petals. The transfer of pollen grains of a flower to the stigma of another flower of a different plant of the same species is called cross pollination or allogamy.
When the pollen grains from the anther of a flower on a plant is transferred to the stigma of a flower on a similar plant it is called cross pollination. Cross pollination - Stigma receiving pollen grains from a flower on the same plant or a different plant. Cross-pollination also called heterogamy type of pollination in which sperm-laden pollen grains are transferred from the cones or flowers of one plant to egg-bearing cones or flowers of anotherCross-pollination is found in both angiosperms flowering plants and gymnosperms cone-bearing plants and facilitates cross-fertilization and outbreeding.
Cross-pollination is the transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower on a different individual of the same species. However pollen cant move on its own so animals or the wind and water in rare cases move the pollen for plants. Contrary to this a flower is pollinated by pollens of a different plants flower in cross-pollination.
There are numerous mechanisms for plants to facilitate cross-pollination such as distyly dichogamy and self-incompatibility. This involves the transfer of pollen by air and water. Production of Synthetic Cross.
In plants hybridisation can be done in two ways. Mating strategies promoting cross-pollination include herkogamy spatial separation of sexual organs including various types of stylar polymorphisms dichogamy temporal separation of male and female maturity ie. Self Pollination Cross Pollination When the pollen grains from the anther of a flower is transferred to the stigma of the same flower or another flower on the same plant it is called self pollination.
Production of Single Cross Hybrids 2. Since cross-pollinated species are naturally hybrid heterozygous for many traits and lose vigour as they. Production of Single Cross Hybrids.
However compared to other mechanisms there seem to be some advantages in promoting cross-pollination by unisexual flowers. 2 development of hybrid varieties. Crossing between two inbreds or varieties is called single cross.
Pollination occurring because of the movement of pollen grains from one flower to another due to agents like animals insects and birds. Example of insect pollination - Rose Euphorbia sps etc. Breeding Methods in Cross Pollinated Crops.
Various methods of cross pollination are entamophily pollination by insects anemophily pollination by wind hydrophily pollination by water zoophily pollination by animals and. It is a type of self-pollination where the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma takes place within the same flower. Sometimes cross pollinating is used intentionally in the garden to create new varieties.
Production of Double Cross Hybrids 3. Here wind acts as a pollinating agent. Due to animal involvement pollen transfer occurs.
Most plants use cross pollination. Cross pollination is when one plant pollinates a plant of another variety. When pollens are delivered to the same flower or different flower of the similar plant it is known as self pollination or autogamy.
Pollination occurring because of the movement of pollen grains from one flower to another due to agents like wind and rain. Those that use insects as pollinators tend to have brightly colored flowers and an attractive scent. Self-pollination occurs when the pollen from the anther is deposited on the stigma of the same flower or another flower on the same plant.
Without the involvement of animals the transfer occurs. Wind pollination can be observed in different grasses maple trees and dandelions. Based on the agents involved in this method there are the following two types as.
What are the different methods of pollination. Wind and insects are two agents of pollination called as Anemoplily and Entomophily respectively. There are two types of pollination which are self auto pollination and mixed cross pollination Self auto pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the anthers of a flower to the stigmas of the same flower or to.
Self-pollination occurs in flowers where the stamen and carpel mature at the same time and. It is defined as the transfer of pollens from the anther to stigma either in the same plant or to a different plant. Example of wind pollination - Grasses Gymnosperms etc.
Geitonogamy is the type of self-pollination where the transfer of pollen grains from the. There are two types of pollination which are self auto pollination and mixed cross pollination Self auto pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the anthers of a flower to the stigmas of the same flower or to another flower in the same plant Mixed cross pollination is the transfer of pollen grains. In contrast cross-pollination leads to the union of unidentical gametes in the breeding system called outbreeding also called outcrossing allogamy or xenogamy Simpson 2010.
And 3 development of synthetic varieties. Types of Self-pollination and Cross-pollination. Cross-pollination can be carried out by wind as well as bees and other birds or animals.
The pollen grains are transferred from one flower to another in different ways which are the pollination by wind the pollination by insects and the artificial pollination. Pollination by air The flowers which are pollinated by the air are characterized by their anthers are hanged to be easily opened by the air and their stigmas are feathery like and sticky to catch. Various types of pollination have also been identified based on the vectors of pollen grains or agents of pollination.
Protandry or protogyny self-incompatibility systems unisexual flowers borne on the same monoecy or different dioecy individuals and various. Plants that use self pollination such as peanuts tend to have smaller flowers. Breeding Methods in Cross Pollinated Crops The most important methods of breeding cross-pollinated species are 1 mass selection.

The Types And Methods Of Pollination In The Plants Science Online
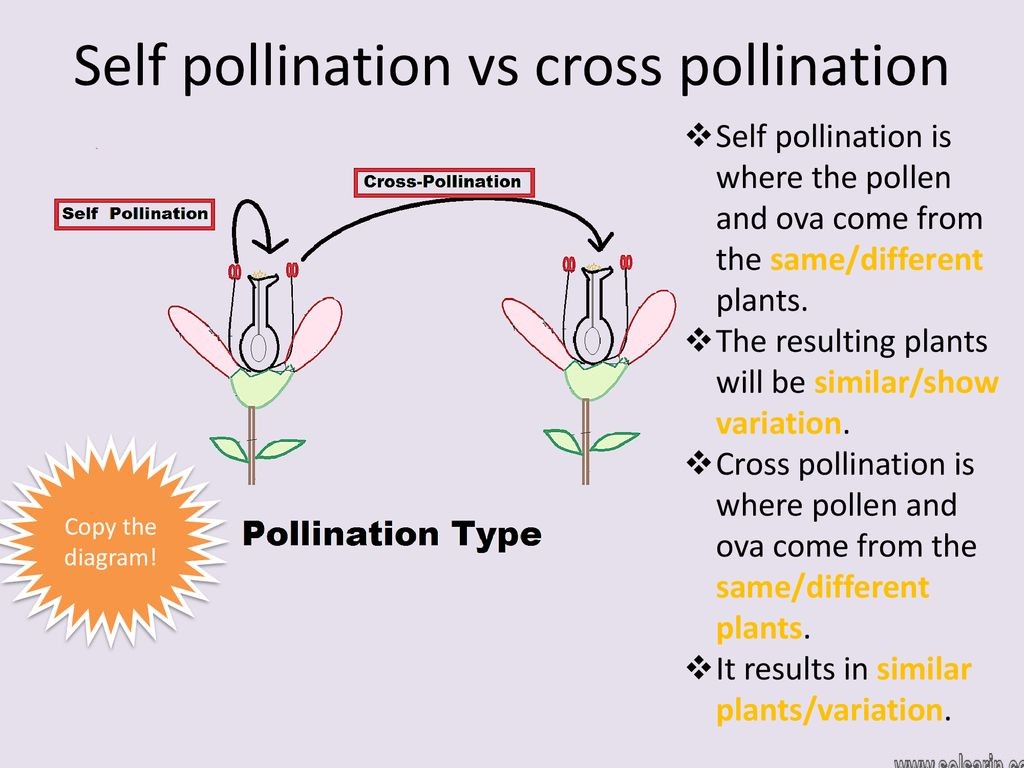
Self Pollination Vs Cross Pollination Perfect Description
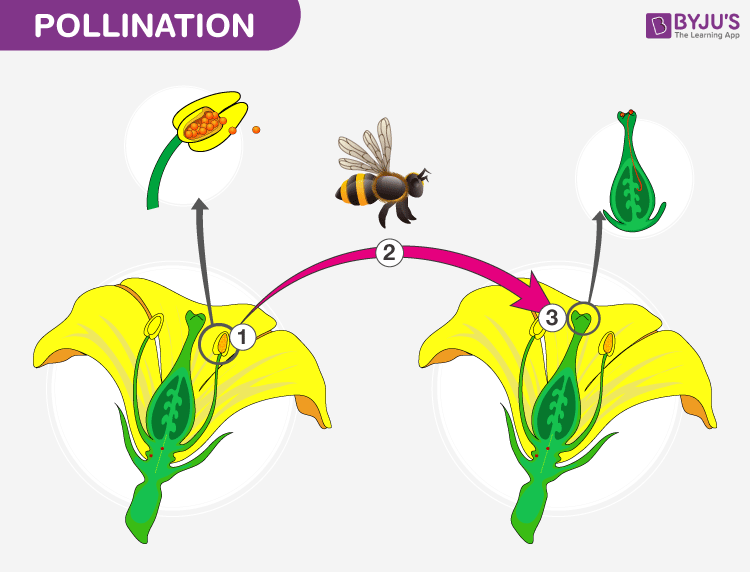
Pollination Types Self And Cross Pollination Pollinating Agents
No comments for "What Are the Different Methods of Cross Pollination Explain"
Post a Comment